The market for robotic process automation (RPA) technology is set to grow at a steady clip through 2030.
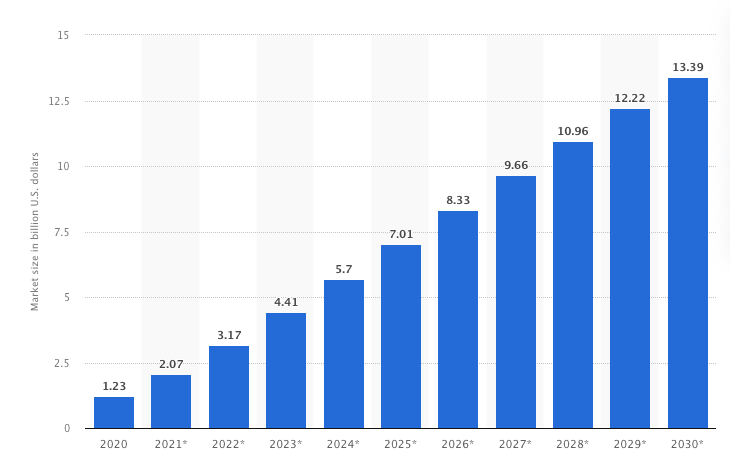
This eye-popping growth projection isn’t hard to believe: RPA technology benefits organizations of all industries, employees across functions, and customers of all shapes and sizes. Moreover, it can be used across your tech stack, from your legacy, on-prem systems to your modern, cloud-based applications.
To help you better understand why RPA software is growing in popularity and how your organization can leverage it, we’ll cover everything you need to know about the software.
We’ll start by defining what it is.
How RPA and enterprise automation differ
Read guideWhat is RPA?
RPA, or robotic process automation, is a type of software that lets you utilize software robots, or bots, to complete UI-level tasks across your applications and systems. These tasks include copying and pasting data, validating data, and sharing documents through various channels.
Related: What is task automation?
What is RPA used for?
While it’s hard to provide an all-inclusive list of the back office and front office tasks that bots can take care of, we’ll give you an idea of their versatility by covering popular use cases across a few functions.
Human resources
- Screen resumes against predefined rules, and then have the bots take the next step for each candidate. Candidates who pass can receive an email around scheduling their first interview, while those who don’t get notified via email that they didn’t make it to the next round.
- As employees submit their timesheets, bots can validate the submissions and email them to the appropriate managers so that they can be reviewed and approved quickly.
- Once a candidate is ready to receive an offer letter, bots can populate your offer letter template using the data from the relevant fields in your ATS. As soon as the offer letter is populated, the bot emails it to the candidate.
Sales/marketing
- Based on information that already exists on the web, bots can help your reps find account information (email addresses, phone numbers, job titles, etc.), and they can then add that information to the prospect’s respective CRM profile.
- The bots can perform competitive analysis (via information found in websites) and then report their findings on a specific cadence. These findings can include anything from changes in a competitor’s pricing to nuanced shifts in their messaging.
- Use bots to crawl RFP and bid sites so that they can, using predefined filters, identify and bubble up lucrative opportunities to the right stakeholders.
Finance
- Leverage bots to extract key fields from invoices, validate them, and then add them to your ERP system.
- Have your bot aggregate data from several sources, upload it into a specific financial report (e.g. a profit and loss report), validate the data, and then share the report with the relevant stakeholders.
- The bot can perform basic reconciliation activities as well as alert the appropriate stakeholders of any transactions that seem dubious.
Related: workflow automation vs RPA
When to use RPA
Though the use cases above are useful applications of RPA technology, there are likely other ways your business can use it.
To identify the most appropriate use cases, you can use the following criteria as a guide:
- The task is repetitive and requires a high volume of work. Your team might have to perform the activity on a weekly, daily, or even hourly cadence. Moreover, your team has to perform an extensive level of work manually (e.g. data entry).
- The task can be completed at any hour. This includes weekends and overnights.
- There are significant adverse outcomes from performing the task poorly. These risks can be both financial (e.g. sending an inaccurate invoice) and legal (e.g. offshore staff accessing customer data).
- Completing the task takes employees away from higher-value work. For employees in technical roles, such as engineering, the opportunity cost is especially high.
- The task is highly-standardized. In other words, it’s easy to train a bot to perform the task.
- There’s little to no changes in how the task gets performed over time. Moreover, this consistency should go a step further to include the apps’ user interfaces.
- The task requires transferring data. We’re also assuming that the volume of data getting transferred is relatively low.
What are the benefits of RPA?
Given its versatility, RPA solutions offer a variety of benefits. Here are a few high-level ones worth highlighting:
1. Provides cost savings
By using bots to perform repetitive tasks, your organization can save a substantial level of man hours and even cut back on hiring employees. This is perhaps best exemplified by a data point that Gartner, the technology research and consulting company, uncovered: The automation technology can save finance teams a whopping 25,000 hours of work, per year.
Related: Issues associated with using RPA
2. Prevents costly errors
Performing manually-intensive tasks aren’t just unpleasant—they also leave employees prone to making mistakes. And although the consequences of these mistakes can vary widely, many carry substantial risks.
Take the process of putting together an offer letter for a candidate: If an employee fills out the fields manually, they might input the wrong salary or job title. And if they do, your organization risks stretching out the recruitment process and losing the candidate to a competing employer.
Bots can avoid mistakes like these, as they can mimic human tasks with 100% accuracy.
3. Increases productivity
Given that bots can operate 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, they’re able to complete more tasks than an employee can within a given time period—whether it’s copying and pasting information, performing calculations, or sharing data.
4. Improves the customer experience
Your customer support reps may be burdened with manual, time-consuming tasks that take their focus away from what’s most important: supporting clients.
Using RPA bots to handle the mundane and tedious day-to-day activities, your support reps are better positioned to respond to clients faster, more thoughtfully, and even proactively—all but ensuring that clients see more value from your product or service.
5. Fosters higher employee retention
Roughly 1 in 4 employees voluntarily left their employer in 2021. And while the reasons varied widely, research by McKinsey found that employees feeling unvalued was a leading cause.
With RPA bots empowering employees to focus on thoughtful, business-critical tasks, employees are being told (albeit implicitly) that their time, expertise, and experience are held to a high regard.
Related: 5 benefits of business process automation
How enterprise automation complements RPA
Despite these benefits, RPA technology doesn’t fully address your organization’s automation needs.
The majority of your workflows operate across teams, applications, and data. Given this distinction from basic tasks, the platform you’d use for automating workflows comes with separate requirements. These include:
- API connectivity across applications and databases as the foundation for any automation
- Customizable chatbots that allow employees to access actions and data in their apps from their business communications platform (e.g. Slack)
- The ability to “listen” for specific business events, where once any occurs, the appropriate actions get triggered
- Centralized governance for IT, allowing them to monitor any integration and automation
An enterprise automation platform not only meets these requirements but it also utilizes the unique benefits provided by RPA technology.
To give you an idea of how this can work, let’s break down how you can use an enterprise automation platform like Workato and an RPA tool like UiPath to automate purchase order processing:
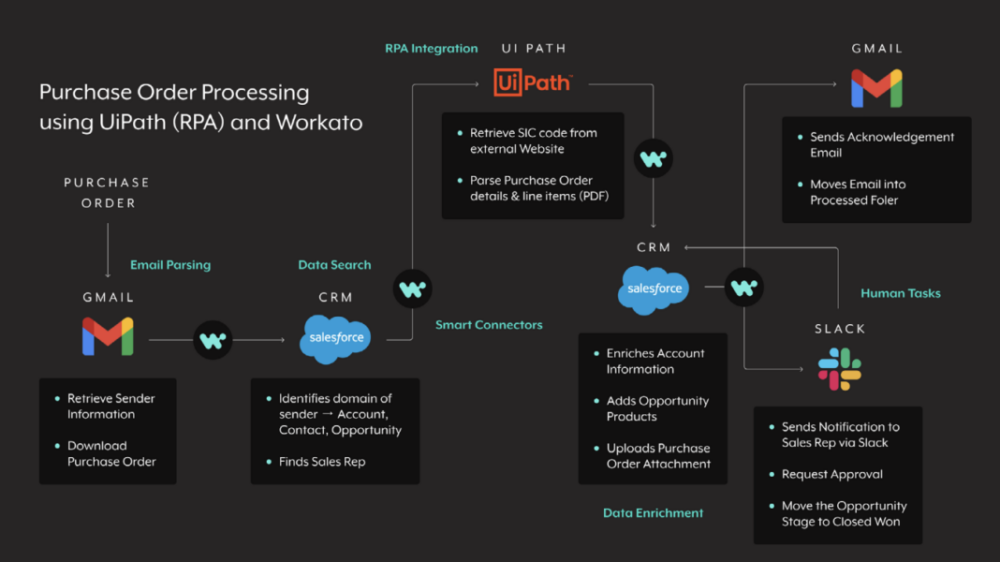
1. Once a signed purchase order arrives in an email service provider like Gmail, Workato triggers the workflow.
2. Workato downloads the signed purchase order and, using the sender’s email address, identifies the sender’s associated pages in a CRM like Salesforce.
3. The RPA bot goes on to search for and retrieve the account’s Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) code, which it uses to enrich the Salesforce account.
4. RPA and OCR technology work together to parse the purchase order, and then a bot goes on to add the appropriate products or services to the opportunity. Meanwhile, Workato uploads the PO to the Salesforce opportunity.
5. Workato’s customizable chatbot, Workbot, notifies the appropriate sales rep of the PO via a business communications platform like Slack. Within the message, the rep has the option of either approving or rejecting the PO.
6. Assuming the rep approves the PO, the chatbot changes the Salesforce opportunity to “closed-won” and sends the client an email confirming that the PO has been processed successfully.
Automate your business processes end-to-end with Workato
Workato, the leader in enterprise automation, provides the following, and much more:
- A low-code UX to integrate your apps and automate your workflows
- Tens of thousands of automation templates (“recipes”) and hundreds of pre-built connectors that can be used as is or customized as needed
- Workbot, a customizable chatbot that enables employees to access actions and real-time data in their apps without leaving their business communications platform
- Recipe IQ, a machine learning-based solution that assists users in building intelligent automations