Productivity and efficiency depends on business process automation. Automation increases overall corporate value by freeing up departments’ teams to concentrate on more strategic projects by automating repetitive operations and lowering manual labor.
It’s projected that about 80% of enterprises will have implemented intelligent automation by 2025, based on current studies. The increasing reliance on automation to stay competitive in the fast-paced corporate climate of today is reflected in this expanding trend.
Why are different departments in an organization aggressively increasing their levels of automation? And how do these automations work in practice?
In this article, we’ll break down the answers to each of these questions and more. You’ll have a complete grasp of process automation and how you can implement it successfully.
What Is Business Process Automation?
The term “business process automation” (BPA) describes the application of technology to automate complicated business procedures to produce significant results like higher productivity, better customer satisfaction, and lower operating expenses. By automating end-to-end workflows with numerous steps and stakeholders, BPA enables organizations to reduce errors, maximize efficiency, and concentrate on higher-value jobs.

While simple task automation deals with specific activities, business process automation addresses entire processes that are essential to a company’s success. Businesses may guarantee accuracy, speed, and consistency in their operations by automating these procedures, which will ultimately lead to increased performance and expansion.
Related: What is a process flow?
Business Process Automation vs. Business Process Management
Business process automation (BPA) and business process management (BPM) are two distinct concepts that are often confused. Understanding their differences is crucial for businesses aiming to streamline operations effectively.
- Scope: BPA aims to increase productivity and decrease manual intervention in a business by automating particular operations or processes. BPM, on the other hand, is a more comprehensive strategy that entails aligning the objectives of the company with the analysis, modeling, optimization, and occasionally automation of entire business processes.
- Objective: The principal aim of BPA is to enhance efficiency by mechanizing monotonous duties. In contrast, BPM aims to enhance the overall effectiveness, efficiency, and adaptability of business operations.
- Implementation: BPA frequently automates specific procedures by using software solutions. BPM necessitates a more comprehensive strategy that includes process modeling, continuous improvement, and monitoring, with automation occasionally being one of the results.
- Outcome: BPA increases productivity in several jobs right away. Long-term strategic gains brought about by BPM facilitate improved decision-making and process optimization throughout the company.
Business Process Automation Examples
Some of the business areas that get benefits from BPA are as follows:
- Finance: Automating invoice processing and approvals, reducing errors, and speeding up payments.
- Human Resources: Streamlining employee onboarding, including document submission and training scheduling.
- Customer Service: Automating responses to common customer inquiries via chatbots, improving response times.
- Supply Chain: Automating order processing and inventory management to ensure timely restocking.
- Marketing: Automating email marketing campaigns, ensuring timely delivery of personalized content.
- IT: Automating software updates and security patches, reducing manual intervention and downtime.
- Sales: Automating lead scoring and assignment to improve the efficiency of sales teams.
How Business Process Automation Works
The process of BPA can be divided into three stages that are detailed below.
Business Process Analysis (BPA)
BPA is the study of how to improve an organization’s internal processes in order to increase productivity and effectiveness. This happens before putting business process automation into practice. This stage is essential because it determines which processes may be streamlined and are most suitable for automation.
Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) and Digital Process Automation (DPA)
IPA combines automation and AI/machine learning to improve decision-making and manage complicated activities. To enhance customer experiences and optimize operations, DPA focuses on digitizing and automating business activities. These developments in BPA provide more intelligent and flexible automation solutions.
Low-Code Development Platforms in BPA
With the use of low-code development platforms, users can write very little code to construct and implement automated processes. By enabling business users to swiftly develop workflows and automate tasks, these platforms increase accessibility to BPA and hasten its deployment.
How to Implement Business Process Automation
Implementing business process automation requires careful planning and consideration. By addressing key aspects of the process, you can ensure a smooth and successful implementation. Here’s how you can get started.
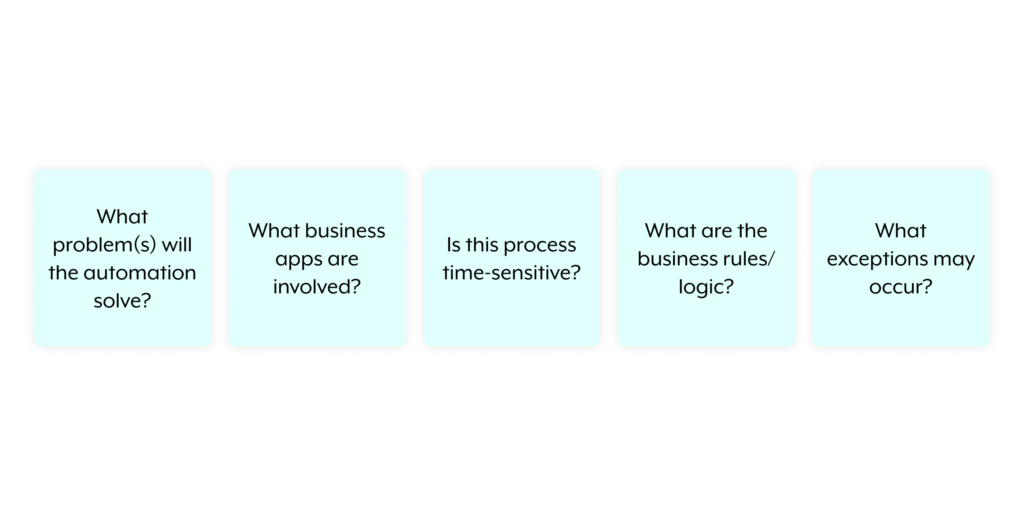
Identify What Problem the Automation Will Solve
Before automating, clearly define the problem you aim to address. For instance, if your goal is to speed up lead routing, focus on variables that impact response times and the quality of follow-ups. This clarity will guide your automation design.
Determine the Business Apps Involved
List all applications that the automation will interact with. By knowing this upfront, you can assemble the right team and ensure all necessary integrations are in place, reducing potential roadblocks.
Assess Time Sensitivity
Evaluate whether the process requires immediate action or can be delayed. For example, lead routing needs instant execution, while end-of-month paperwork allows for more flexibility. This will help you select the appropriate triggers for automation.
Define Business Rules and Logic
Understand the specific rules and logic that will govern the automation. This might include data validation, transformation, or aggregation. Knowing these requirements ensures that your chosen automation tool can handle the necessary functions.
Anticipate Potential Exceptions
Consider potential issues, such as system outages or missing data. Planning for these exceptions in advance will help you build a robust automation that can handle unforeseen challenges without disrupting operations.
Related: What is business process integration?
Benefits of Business Process Automation
Now, let’s break down a few of the benefits that come from automating your processes.
Data Silos Break Down
Data silos, or when data is locked in specific apps that only certain employees can access, cause all kinds of issues.
They can leave employees unaware of certain types of data, and thereby unable to benefit from it; they can force employees to request data from their colleagues, which can delay their timeline for receiving it; and they can discourage employees from requesting access to data, as the expected delay can significantly diminish the data’s value.
By integrating your systems and implementing workflow automations that enable the data to move seamlessly across your tech stack, you can easily remove these silos and the negative consequences they created.
Business Processes are Transformed
Process automation offers opportunities to reenvision how your teams execute their operations.
To illustrate this, let’s use an example. Say your sales reps need to identify clients who are ready to spend more with your organization. Moreover, they need to build out presentations to persuade these clients to make additional investments.
Instead of having reps manually comb through their list of accounts to identify those worth pitching, where they’d then build out slides for each client they pitch, you can put together the following business process automation:
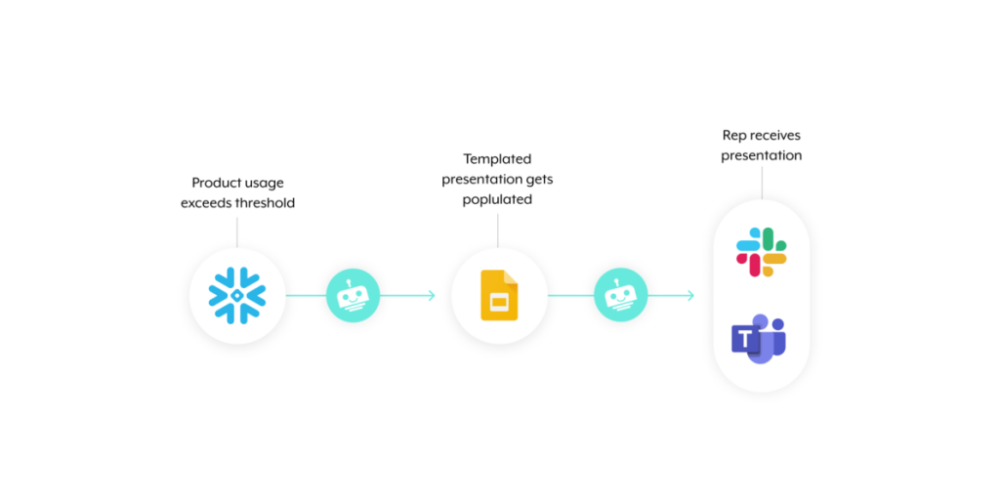
1. Once the client’s level of product usage exceeds a certain predefined threshold, the workflow gets triggered.
2. A platform bot collects information on that client from various systems, which it uses to populate a templated slide deck.
3. The platform bot shares the slide deck with the assigned sales rep in their business communications platform, whether that’s Slack or Microsoft Teams.
Employee Experiences Improve
The previous benefits already imply this, but it’s worth writing out: Well-executed process automations can dramatically improve the employee experience.
They allow employees to avoid repetitive tasks that are less than pleasant to perform (e.g., data entry), where instead, employees can focus on the thoughtful, business-critical work they value. In addition, automations like the example above improve employees’ decision-making abilities and, therefore, their chances of being successful.
Customers Receive Best-in-Class Support
There’s a seemingly endless supply of research that points to the value of providing top-notch support, from increasing the prices of your products and services to boosting positive word of mouth to outperforming competitors (in terms of revenue growth).
So how do you provide support that both fuels customer satisfaction and lets you reap these business benefits? By automating your support processes.
To help paint the picture, let’s use a BPA example that looks to accomplish the following: enable customer success managers (CSMs) to identify and support clients who struggle to get enough value from your product.
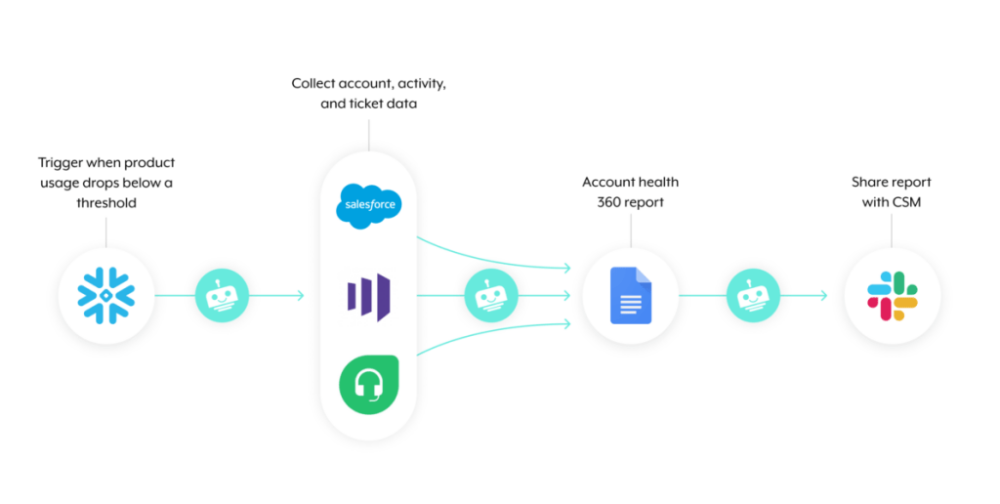
1. Once a client’s level of product usage drops below a certain level, the workflow gets triggered.
2. A platform bot collects data on the client from various sources, and it goes on to use that data to populate a templated account health 360 report, which lives in a Google doc.
3. Once completed, the platform bot shares the report with the assigned customer success manager (CSM) via your business communications platform. From there, the CSM can respond quickly and in a way that inspires the client to use your product further.
Related: How customer-facing teams can leverage product intelligence
Challenges of Business Process Automation
Business process automation offers numerous benefits, but it also comes with challenges that can lead to project failures. Here are some common reasons why automation projects might fail:
- Lack of Clear Objectives: Automation projects often fail when goals are not clearly defined, leading to misaligned expectations and outcomes.
- Inadequate Change Management: Failure to manage the transition effectively can result in resistance from employees and poor adoption rates.
- Complexity of Integration: Integrating automation tools with existing systems can be complex and, if not handled properly, can cause disruptions.
- Insufficient Testing: Skipping thorough testing can lead to unforeseen issues during implementation, causing delays and additional costs.
- Overlooking Maintenance: Automation requires ongoing maintenance. Ignoring this can lead to outdated processes and potential failures.
- Underestimating Costs: Not accounting for the full cost of implementation, including hidden expenses, can strain budgets and derail the project.

Conclusion
After reading this article, you now know the fundamentals of business process automation, including its definition, operation, and successful application. Gaining insight into the advantages and difficulties will enable you to encourage creativity and efficiency in your company.
Leading the way in enterprise automation, Workato can help you optimize your workflows with a low-code/no-code platform that enables IT and business teams to collaborate more effectively. Workato guarantees that your automation efforts are scalable, safe, and effortlessly integrated into your current workflows with hundreds of automation templates, prebuilt connectors, and AI-powered bots. Moreover, the platform offers:
- Hundreds of thousands of automation templates and hundreds of pre-built connectors so that your team can build integrations and automations faster and with minimal customizations
- Enterprise-grade governance and security so that citizen integrators can use the platform without compromising sensitive, business-critical data
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning-powered platform bots that can bring automations directly to your business communications platform, whether that’s Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Meta Workplace