In business, there’s always time that can be saved and dollars that can be better spent. The more fluidly and efficiently the mechanism runs, the further it will go.
Business leaders know that the gears that comprise the mechanism include more than just the right people in the right positions. Now, more than ever, technology plays a massive role in day-to-day operations. The right digital tools don’t only assist the human capital that powers products and services. The right digital tools provide their own capabilities that allow people to do more and allow companies to do better.
APIs have emerged as a critical component in an organization’s operations.
To more fully understand just how critical APIs are for an organization’s growth, let’s consider just one of the key features of APIs: they can be relatively easy to create and manage. This has been leveraged across the web, from independent developers looking to create successful APIs, to major corporations like Twitter looking to expand their reach by opening access to their platform via external APIs.
In this article, we’ll explore some reasons why your organization should build an API, provide you with tools for developing APIs, and share best practices for API development.
Before we go too far, let’s start by defining what an API is.

What Is an API?
For those who need it, here’s a quick refresher on APIs—not just what they are, but how they work.
An API, or application programming interface, is a set of instructions or functions that allow two systems to exchange data or functionality.
First, a call is made to a data source—think of this as a database that houses information that an application or user would want. The call is made with the API, and just as a keypad on a phone would operate as the interface for making a phone call, the API is the interface for one service to access data from another.
Again, just as a phone number would act as a format that defines the terms of the communication in a phone call (who is being called), an API uses a specific format to specify the type of request being made between systems; in this case, the request is either to Get, Post, Put, or Delete information.
After the request is processed, the API sends a response in the form of a successful execution.
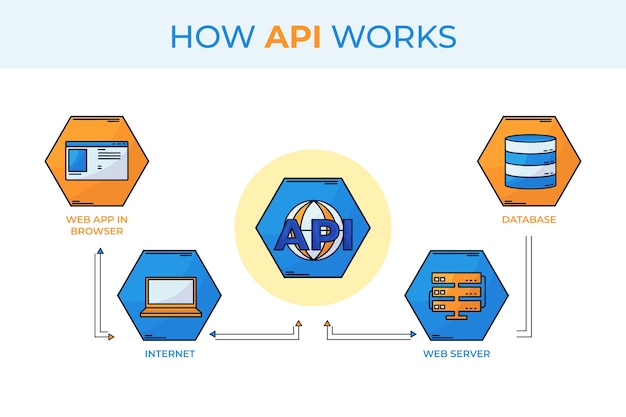
There are two main types of APIs:
- REST (representational state transfer) APIs
- SOAP (simple object access protocol) APIs
Just as the process of how APIs work is an easy one to understand, the argument for why every company should be using APIs is an easy one to make.
3 Reasons Why You Should Build an API
The way in which APIs are transforming how business is done might make some nostalgic for how social media revolutionized how people connected with each other and the world.
The social media model was simple: make connections easily. With Facebook, for example, Person A created an account and then connected with two friends, who themselves were each connected to four friends. In a matter of minutes, and without much effort, Person A had ten connections.
Similarly, APIs make making connections easy, though in this case, instead of connecting people, they connect apps or services.
One platform, let’s say a local bookstore, provides on its website a way for users to not only browse their inventory, but, through an API, also browse the inventory of a warehouse from which the local bookstore can order if it does not have a desired title in stock. In this example, the API connects customer with product, resulting in a profit for the local bookstore.
It’s difficult to imagine a business that would not benefit from utilizing APIs. Let’s look at the three top reasons for building an API.
Related: Why API integration is critical
1. APIs Can Increase Usage of Your Platform
Web users are increasingly sophisticated in their tastes for services that are not only intuitive, but also anticipate their needs and preferences. A robust ecosystem of APIs on your platform is necessary if you’re going to keep these users—and the suite of app allegiances they each carry—engaged with your product. This makes for a more used (and “stickier”) service.
Example
Evernote is a cloud-based note taking and organizing app that allows users to create, customize, label, search, and send notes. This can be a useful service to many to have all of one’s notes expertly curated and easily accessible through just one app. However, most user footprints extend across many apps and, therefore, their data does not exist in a vacuum. Through APIs, the user can distribute certain notes via their Gmail, Slack, or Microsoft Teams accounts. This functionality retains the Evernote user instead of losing him or her to another service.
2. APIs Can Connect Your People and Streamline Your Business Processes
When integrated into your business applications and processes, APIs provide efficiency and connectivity across lines of business. This translates to solutions for your clients.
Example
When your company’s help desk receives a ticket through ServiceNow, depending on the source or level of urgency on the ticket, it can be sent to the appropriate individuals in the organization. If the ticket came from a prospective client, an API can facilitate communication with the client’s primary contact in sales. And if the ticket needs immediate action, an API can prioritize the request through a platform like Slack.
3. APIs Can Satisfy Your Tech-Savvy Audience and Drive Your Revenue
Once you’ve built a product people love, you can capitalize on their enthusiasm by providing premium features through APIs.
Example
Canva, a cloud-based SaaS, is a graphic design platform that allows users to create and publish a wide range of visually-enhanced content, from social media ads to résumés. Canva offers generous functionality with its free version, within which many apps are connected via APIs (e.g., users can post their creations easily to Instagram or MailChimp). But Canva’s premium features, such as advanced photo editing tools, exist behind a paywall. Many Canva users will want to use the platform to create professional-level designs, and will pay for the API that will allow them to do it.
Related: 4 reasons to adopt API management
List of Potential Tools for Developing APIs
As APIs have exploded onto the digital transformation scene, so have the tools used to create, monitor, and test them. The following services and platforms offer a range of API development capabilities and tools, and are provided below in one of three categories.
No-code development tools:
- Sheetsu
- Bubble
Low-code development tools:
- Restdb.io
- Postman
API testing services:
- BlazeMeter
- Loader
Every good build starts with a solid plan, so let’s take a look at some of the best practices in API development.
Related: A list of web APIs and web service APIs

Challenges of API Development
Although there are various benefits or reasons why you should use APIs, there are also some challenges and drawbacks associated with API developments. Below are some challenges related to API development.
Versioning
As important as introducing new features and integrating with new applications to meet evolving user needs and stay competitive in your industry, ensuring a proper API versioning strategy is more important. This will ensure your developers and users have a smooth experience.
A terrible API version strategy will disrupt backward compatibility and integration, cause break changes, and complicate version maintenance for your users. It is also important that users know the version of your API they’re accessing so they know the features and limitations of what they’re working with.
Security
APIs expose data and information to the public; thus, protecting it from unauthorized access and data breaches is important, especially if publicly available online. One way to do this is by implementing throttling and rate limiting, a method that limits the number of requests a client can make. Another way would be to conduct security audits and implement validation systems—SQL injection protection, authentication mechanisms like API keys and OAuth2, and HTTPS to ensure data encryption and thwart man-in-the-middle attacks.
API Orchestration
Deploying and managing various API endpoints on a large scale can be pretty overwhelming. Hence, it’s handy to have an effective API orchestration plan to manage requests and calls across these APIs. Developers typically use API gateways, microservices architecture, middleware, or workflow automation tools like Workato for their integration and automation needs.
API Integration
The whole point of APIs is to aid communication and data sharing between systems, services, and databases. However, every system and service comes with its own formats and protocols, which adds complexity to the integration process. This issue can, however, be migrated by taking an API-first development approach when developing your service. Another option is to ensure you have automated test frameworks to test endpoints, up-to-date documentation, and that you adopt standard protocols such as REST, SOAP, or GraphQL.
API Documentation
You are building your API so developers can consume it. Hence, you must have user-friendly, detailed, and clear documentation to ensure your users can effectively consume your APIs. This is also important for ensuring your API is available and users have a great developer experience. You can solve this by having quick start guides, SDKs, tutorials, and sandboxes within your docs so users can experiment with your endpoints.
Best Practices for Building an API
Here are some of the most important considerations in API development:
Authentication
A secure API is one built with authentication and authorization protocols to protect data at the receiving end of the API call, control who can gain access to the API, and limit the amount of data transferred. Three common methods of authentication are HTTP Basic, API Keys, and OAuth.

Documentation
It’s important to provide clear and comprehensive instructions for developers who want to use or integrate with your API. Your documentation should act as a reference manual, and include the functions, classes, return types, and arguments of your API.
Need for Speed
A major incentive for using REST APIs as opposed to SOAP is their potential for speed. Some APIs will need to return responses much faster than others—a dashboard that displays real-time stock market data, for example—and knowing this prior to building the API will determine which API type to develop.
Rate Limiting
Capping the number of calls (or “requests”) a user can make to your API over a period of time (either seconds, minutes, days, weeks, or months) will ensure that the call volume doesn’t slow down performance by exceeding demand expectations and therefore clogging your servers or overwhelming your apps.
Analytics
You can build in data logging as a feature of your API to capture requests made (the popularity of the API) and responses failed (the need to fix the API). The more you apply performance data to your API development, the more successful you’ll be!
Testing
A critical step prior to launch is testing the API for reliability, performance, and security. Developers can test their APIs with their own code or, as mentioned in the previous section, can use services such as BlazeMeter and Loader.
When Not to Use an API
As beneficial as APIs are, there are instances when APIs are not the best or most practical options for integration. For starters, when your application and system don’t need to interact with other services, share data externally, require basic functionality, or manage data without external calls. In this case, using an API adds unnecessary complexity.
When APIs are not the best choice:
- Data breaches are costly in heavily regulated industries, like healthcare or finance, with strict data regulations. Thus, API should be avoided when necessary to reduce any compliance risk.
- Monolithic systems, because the components are designed to work together closely. Thus, APIs will bring complexity, reduce flexibility, and increase resource usage. Internal function calls or direct database access are a much better approach in these cases.
- APIs have network latency and dependencies on external service issues, impacting user experience in real-time and performance-sensitive applications like gaming and trading platforms.
How to Test APIs
API testing is all about ensuring your API is running and serving its users in terms of functionality, security, reliability, and performance. There are various ways to test your APIs, including unit, integrated, security, performance, and functional testing.
Testing is a huge and important topic in itself; thus, you should check out this video on how to build, test, and monitor APIs with Workato.
Related: A guide to successful API testing
FAQs
What is GraphQL, and how does it relate to APIs?
GraphQL is a query and manipulation language developed by Facebook that allows users to request the specific data they need (declarative data fetching). It reduces over- and under-fetching scenarios, making it perfect for developers working with complex data structures.
Unlike traditional APIs, GraphQL is seen as more client-driven because It allows developers to develop APIs that service specific needs. These APIs can also integrate with other APIs and databases, letting your front-end developer rely less on back-end changes, as they can define the response structure they want.
What are cloud APIs?
Cloud APIs allow users to access cloud computing services, from your compute infrastructure and storage resources to your monitoring tools. They transfer data between and across cloud services and on-premise applications through a client-server model. They are often used for non-core functionalities like authentication, payment processing, or data storage.

There are two main types: Infrastructure-level and application-level cloud APIs.
How do cloud APIs work?
This depends highly on the use of the API and its protocol. However, in general, these APIs send and receive requests between the cloud and on-premise applications by:
- The API client sending a request (API call).
- The endpoint receiving and authenticating the request to ensure its safety and that the client can access the data.
- The endpoint sending back the requested data.
What are the benefits of cloud APIs?
Cloud APIs offer benefits such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and performance. These are because they leverage cloud resources, operate on pay-as-you-go models, handle updates, integrate with other cloud services, and have high availability and reliability in case of failure.
What are the challenges of cloud APIs?
For starters:
- Cloud APIs are highly dependent on network connectivity.
- Governance can be difficult, as the cloud provider must meet compliance requirements.
- Possible vendor lock-in.
- Performance variability due to shared resources, varying loads, and network latency.
Need a Better Way to Manage Your APIs?
Workato, the leader in integration-led automation, offers an API management platform that allows your team to manage the full lifecycle of APIs, both internally and for external partners.You can see the platform in action and better understand how it can help your organization by scheduling a demo with one of our expert automation advisors!
