Data integration is merging data from several sources into a single, cohesive perspective. This activity makes it easier for companies to access and use their data. An efficient method of integrating this data is essential since, as companies expand, more apps are employed for data collection and storage.
Sixty-eight percent of data collected is generally unused, with the average organization deploying roughly 300 SaaS apps, according to IDC research. Your team can make better decisions and work more efficiently by utilizing data integration to assess this information fully. This post will discuss the value of data integration and several strategies you can use to implement it properly.
Related: What is iPaaS? Integration Platform as a Service explained
What is data integration?
Gathering information from multiple internal and external sources, converting it into a common format, and then putting it all together in one place—like a data warehouse—is known as data integration. Because of this centralization, teams from many departments can access, examine, and use the data to make well-informed decisions. It ensures that all data is unified and simple to work with. This is especially helpful for businesses working with complicated, divergent data environments. Data integration also includes different methods depending on the organization’s needs. These methods include:
- Data Replication: Copies data from one system to another to ensure consistency across multiple environments. This is useful for backup and disaster recovery.
- Data Virtualization: Creates a virtual view of data from multiple sources, allowing access and querying without physically moving the data.
- Data Ingestion: Importing and processing data into a storage system. This can be either in real time or in batches, to make it ready for analysis.
- Data Warehouse Automation: Automates the management of data warehouses, including ETL processes, to enhance efficiency and reduce manual errors.
- Data Streaming: Continuously captures and processes data in real time. This is essential for applications that need immediate insights, like IoT or financial trading.
- Data Governance: Manages data quality, security, and compliance, ensuring that data is consistent, reliable, and used responsibly across the organization.

Data integration example
To clarify how data integration works in the real world, let’s cover a common example:
Data integration works well in numerous contexts. For instance, in the context of business intelligence (BI), analysts can analyze and make intelligent decisions from high volumes of data. In the context of big data, organizations that collect an immense amount of information over time—think Amazon or Apple—can manage and analyze that info effectively.
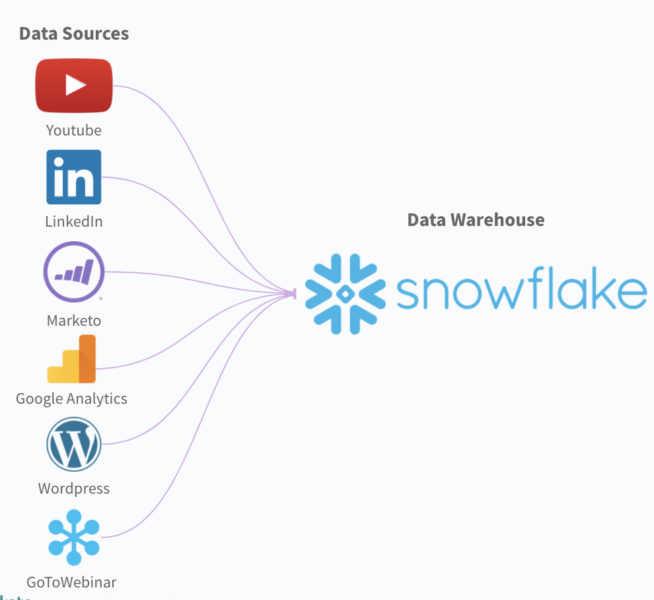
Marketing teams use an ETL tool to collect information from various data sources. For example, social media channels, analytics platforms, marketing automation platforms, etc. The tool then standardizes the data before putting it into a data warehouse, like Snowflake.
Once the data lives in the data warehouse, your team, along with colleagues in other functions, like sales, can access the data in a unified view. You and your colleagues can then query and retrieve the data, build reports with it, etc., all with relative ease and in ways that allow you to track and better understand the performance of various marketing activities.
Note: Data integration shouldn’t be used synonymously with application integration. The latter involves integrating applications directly so that their data stays in sync.
Real-time data integration
Real-time data integration involves the immediate collection, transformation, and movement of data as it’s created. This approach is commonly used in situations where quick access to updated data is critical. For example, in financial trading, where split-second decisions are essential, or in logistics, where real-time tracking ensures optimized operations. By processing data in real time, organizations can react faster to changes, improve operational efficiency, and gain timely insights for strategic planning.
Why is data integration important?
Based on our definition of data integration, let’s explore some of the reasons why it’s important below.
Removes data silos in your organization
Data silos, or when only certain employees have access to specific data points, can create all kinds of unintended negative consequences. This includes having employees:
- Re-enter data in multiple apps
- Hop between apps to find information
- Miss out on critical insights
- Misaligned on key areas
With integrated data, your organization can instantly eliminate data silos, as employees can now access a unified view of all the data across the organization’s apps. This allows individuals to be more productive in their own work. Also, to work within their team and across various functions more effectively.
For example, by allowing your sales reps and your marketers to view the same set of data on leads, the teams can work in tandem to intelligently nurture and pursue target accounts.
Related: The benefits of integrating customer data
Saves your team from performing tedious tasks
Instead of forcing employees to move between applications to find data or ask their colleagues for it, they can easily find the information themselves. This saves employees time, helps them avoid distracting their peers, and allows them to focus more on business-critical tasks instead.
For instance, if lead data is readily accessible, sales reps can allocate more time on prospecting activities or on personalizing demo presentations—versus finding information on leads.
Ensures that your data is reliable and easy to analyze
If forced to find and gather data manually across apps, employees may make common mistakes that can be attributed to human error, such as collecting the wrong set of data or collecting data that’s out-of-date. When this happens, employees can be led toward poor decisions that harm their performance, the experience of clients, and even their employer’s bottom line.
By moving your data to a data warehouse instead, the data can be continually updated in real time and can be made easily available for analysis—whether your team is looking to compile specific reports, run queries to find key data points, perform more robust business intelligence, etc. This all but ensures that your data quality is up to par and that your team is empowered to use the insights provided.
Enables your team to get more out of each application
Now that a greater number of employees can access and use data from each application. Your apps are more likely to deliver a higher ROI for your business.
For example, if data scientists can easily access sales reps’ activities in your customer relationship management (CRM) platform, they might be able to build a model that can determine the types of sales activities that lead to higher conversion rates; and if account managers can access clients’ support tickets as they come in, account managers can then better identify when an account is at risk of churning or open to spending more.
Related: 6 benefits of data integration

How data integration works
The process of integrating data involves developers, architects, and data engineers working together. Data engineers create and manage data pipelines, making sure that information moves smoothly from several sources to the intended location. Data architects outline the structure and organization of data storage. Meanwhile, developers construct and manage the systems and tools that enable integration.
Change Data Capture (CDC), which recognizes and records data changes in real time, is essential to this procedure. This technique makes sure that the data in the target system is always current with the source, which is important in situations when timely data is required, such as inventory management or financial transactions.
The challenges of integrating data
Reaping the benefits of integrated data is far from easy. Here are just a few reasons why.
Integrations built in-house are resource-intensive to build and maintain
The process of implementing and maintaining integrations between apps and your data warehouse requires involvement from your dev team—as they’d be tasked with writing custom code that can support the connections. This can take them away from other tasks that they’re uniquely equipped to solve, such as building out new product features or enhancing existing features.
In addition, your organization is left vulnerable when the few developers who understand a custom-built integration (or point-to-point integration) leave the company. The remaining employees may not be aware that the integration exists, let alone understand how it works. This increases the chances that the integration fails to work properly and that your team then struggles to fix the integration quickly.
The result? Your employees may no longer get the data they need to perform their day-to-day work. Also, your clients may not receive the types of experiences they expect and need.
The ever-changing ecosystem of saas applications complicates integration efforts
Organizations are dropping more than 30% of their apps on a yearly basis. To accommodate this evolving app landscape seamlessly, organizations need a means for integrating data that’s flexible, fast, and easy—all of which isn’t possible through point-to-point integration.
The number of integration opportunities is rising at a rate that’s hard to keep up with
As organizations adopt more apps, the data that can be integrated and the workflows that can be automated grow as well. Unfortunately, given the complexity around building and maintaining point-to-point integrations, your team would have a hard time at making the most of these opportunities.
Accessing and understanding data from legacy systems can prove difficult
Considering the stagnant nature of legacy systems, many offer limited options around connectivity. Furthermore, employees who are less familiar with a legacy system’s data model can have a difficult time making sense of its data. This makes it challenging to export the system’s data and translate it correctly to your data warehouse, among other places.
The semantic integration problem
When data from many sources cannot be properly combined because they don’t have a common meaning or context, the problem of semantic integration occurs. Variations in data formats, terminologies, or architectures between systems are frequently the cause of this problem. To solve it, data definitions must be aligned and consistency must be ensured, frequently through the use of standardized data models and data governance procedures.
Related: 5 data integration challenges and how to solve for each
Data integration tools
To help you overcome at least some of the challenges above, you have a few data integration solutions to consider:
- An extract, transform, load (ETL) tool: This type of tool allows you to standardize the data before putting it into the data warehouse. That way, once the data gets loaded there, it’s cleaner, consistent, and ultimately easier to analyze and get value from.
- An extract, load, transform (ELT) tool: This tool operates similarly to an ETL tool, only that it transforms the data once it lives in the warehouse. Deciding between an ELT or ETL approach largely depends on the types of transformations you want to implement. If they’re less complex, you would generally go with an ELT approach.
- An integration platform as a service (iPaaS): This cloud-based platform can connect your SaaS apps and on-premise systems and allow the data to flow freely between them. A key distinction here is that instead of just providing a single, unified view of all the data, an iPaaS can also sync data across the apps your employees use.
As an alternative option, you can turn to an integration-led automation platform.
Related: Application integration and data integration—how they differ and where they overlap

Conclusion
Any organization that wants to fully utilize its data across several systems and apps must implement data integration. Businesses may improve operational efficiency, make better decisions, and seize new development opportunities through the proper integration of data. A well-thought-out data integration strategy is essential for remaining competitive in today’s data-driven environment. That could mean a strategy involving real-time data integration, the use of sophisticated automation tools, or tackling everyday issues like semantic integration. Through the implementation of appropriate tools and methodologies, your corporation can guarantee that its data is not merely gathered, but also effectively utilized to generate significant business results.
For example, an integration-led automation platform offers the following (and much more):
- Load high volumes of data into your data warehouse
- Build powerful integrations and automations between cloud apps, on-prem systems, databases, etc., without writing a single line of code
- Browse and pick from a library of customizable, pre-built connectors and automations
- Leverage enterprise chatbots that enable your team to work in their apps and automate their workflows without leaving their business communications platform (e.g. Slack)
Learn how Workato, the leader in integration-led automation, can help your team by scheduling a demo with one of our experts!